
Congenital RenalAnomalies in Adults
Mindy M. Horrow, MD, FACR
Director of Body Imaging
Albert Einstein Medical Center

Outline
•Abnormal Kidney
•Location
•Fusion
•Duplication
•Other

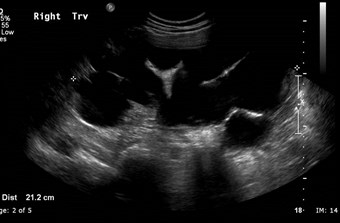
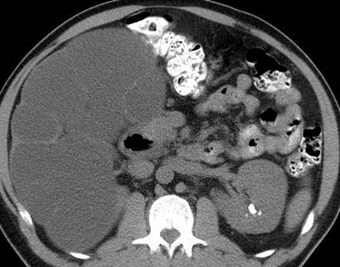
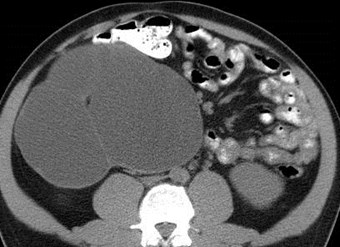
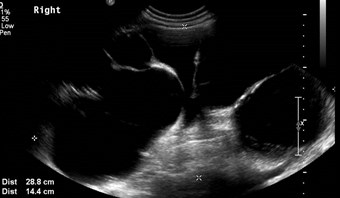
Ureteropelvic JunctionObstruction

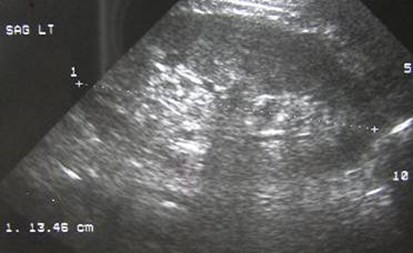
Chronic R UPJ Obstruction
Compensatory Hypertrophy L Kidney

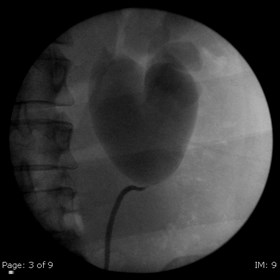
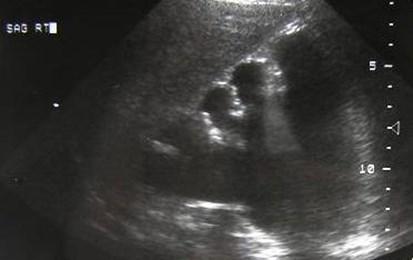
Acute left flank pain
Acutely obstructing L UPJ

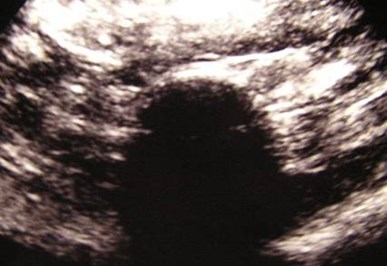
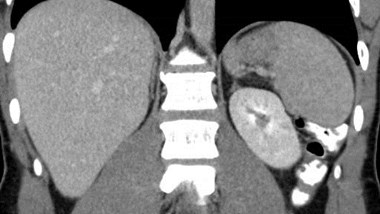
Right Kidney
Left Renal Fossa
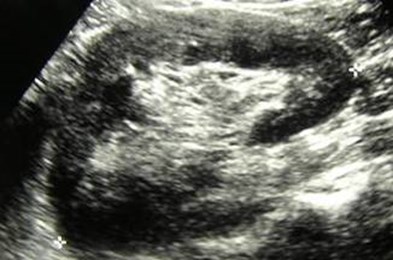

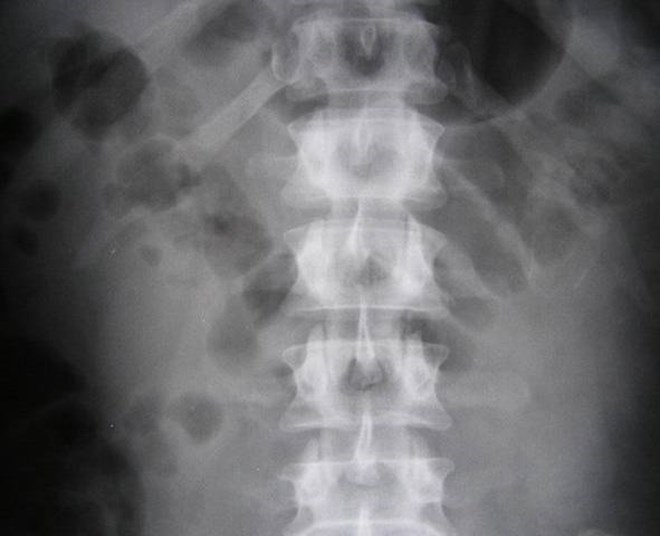

Multicystic dysplastic leftkidney

Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney
•Several Forms
–Classic- random configuration of cysts
–Hydronephrotic form- discernable dilated renalpelvis surrounded by cystic structures
–Solid Cystic Dysplasia- smaller cysts with greateramount nonfunctional parenchyma
•Competing Theories
–Ureteral obstruction in utero
–Abnormal induction of metanephric blastema byureteric bud.
–(In both MCDK and UPJO, left kidney more ofteninvolved than right)

Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney
•Bilateral MCDK incompatible with life
•50% with other urinary tract anomalies: UPJO, refluxin contralateral kidney (15 – 20%)
•Affected kidney involutes or decreases in size in 60-70%, which can take up to 20 years or occur beforebirth.
•Rarely become symptomatic

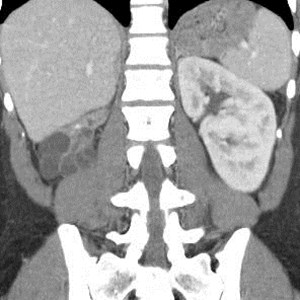
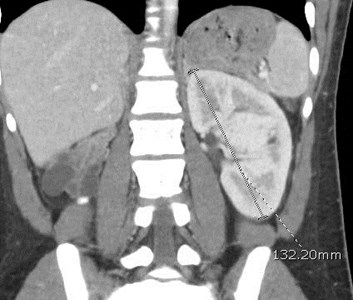
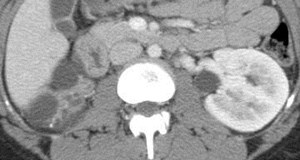
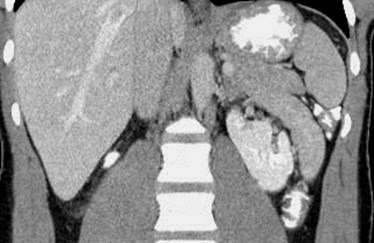
Right Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney

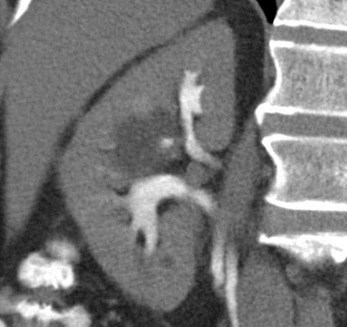
Duplicated Right Collecting System
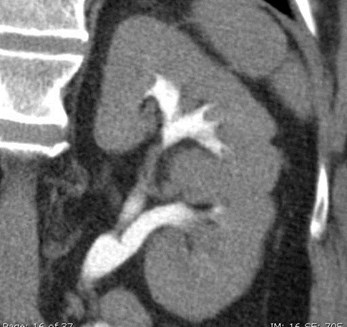
Bifid Left Collecting System

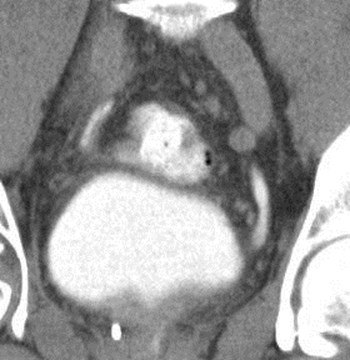
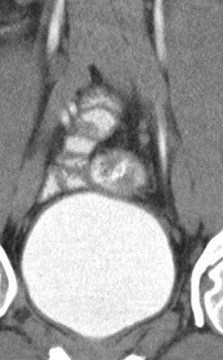
Right ureters join before bladder =Incomplete Duplication

Duplication of Ureters = RenalDuplication
•Most common anomaly of urinary tract
•Incomplete duplication three times morecommon than complete, which is reportedto occur 1/500
•May be discovered in utero, in childhoodor less frequently in adulthood or autopsy
•Duplication is a common cause of anenlarged kidney

Incomplete Duplication
•Embryology not well understood but mayoccur when single ureteral bud branchesbefore reaching metanephric blastema.
•Duplicated ureters unite at variable distancefrom kidney with only one ureteral orifice
•Ureteroureteral reflux is common buttransitory.

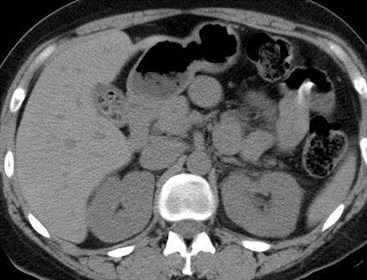
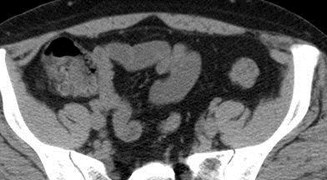
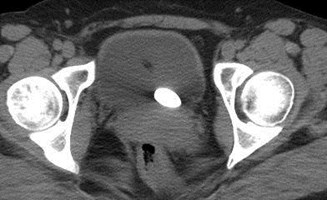
Acute Left Flank Pain

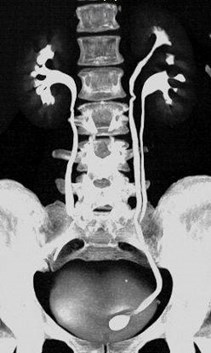
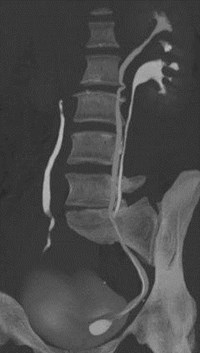
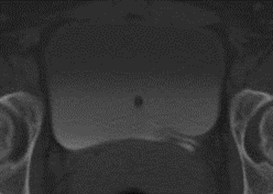
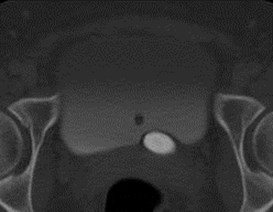
Complete left ureteralduplication with calculusin ureterocele

Complete Duplication and theWeigert-Meyer Rule
•Ureters arise from Wolffian ducts.
•Ureter of lower pole arises inferiorly and isincorporated into developing bladder first,inserting superiorly and laterally to ureter ofupper pole
•Ureter of upper pole remains with wolffianduct longer, inserting more inferiorly intobladder or wherever remnants or derivativesof wolffian duct are found.

Complete Duplication
•Ureters arising from normal position onWolffian duct have normally positionedureteral orifices and normal upper tracts.
•Upper pole usually consists of only a fewcalices or compound caliceal group drainedby single infundibulum, while lower pole hasmost of the calyces.

Ectopic Ureterocele
•Dilatation of intravesical component of upper poleureter (ureterocele) is usually associated withdilatation of ureter and calyces
•Occurs 8 times more frequently in women
•Appears on US as thin walled “bleb” or “cyst” inbladder base at ureteral orifice
•Often associated with an obstructed dysplastic upperpole moiety
•Ipsilateral ureter, pelvis and calyces may be normalor extremely small.

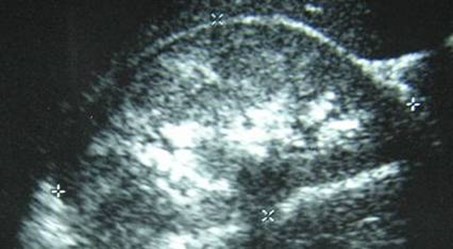
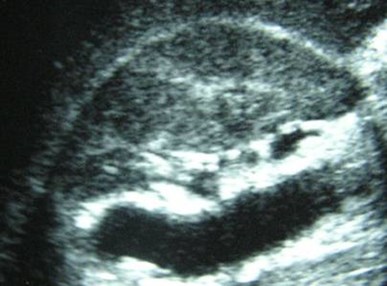
R Sag lateral
R Sag medial

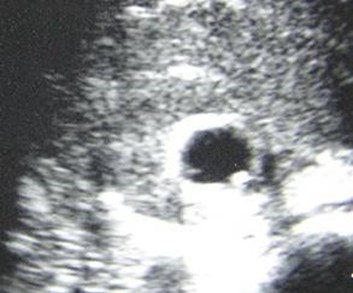
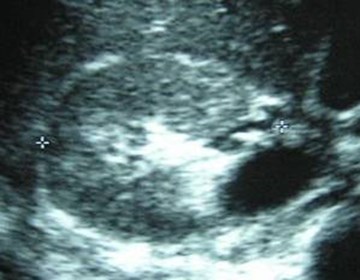
Trv superior pole
Trv mid pole

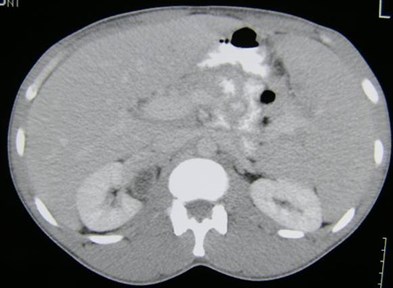

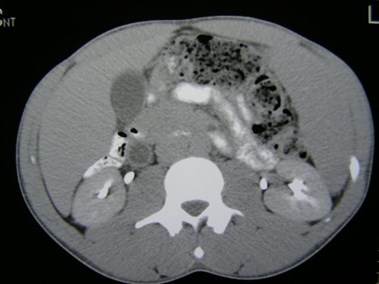
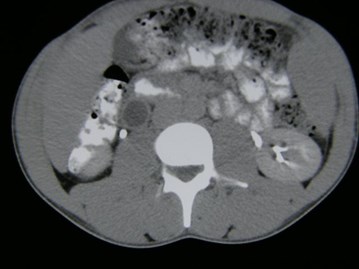
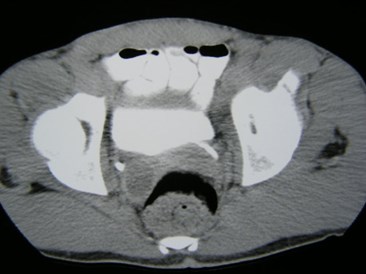
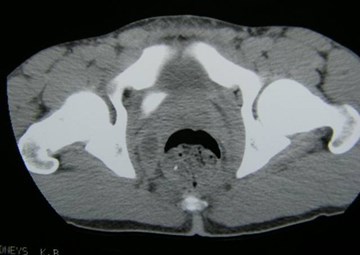
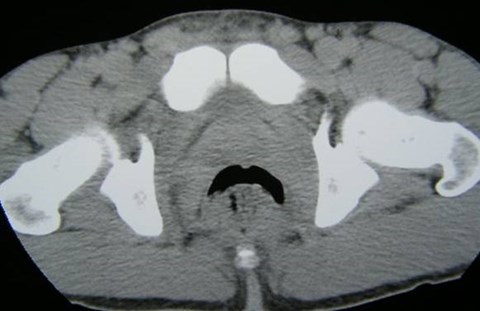

Duplicated Collecting SystemRight Kidney
Chronic obstruction upper pole
moiety, with ectopic ureterinserting into prostatic urethra

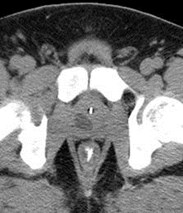
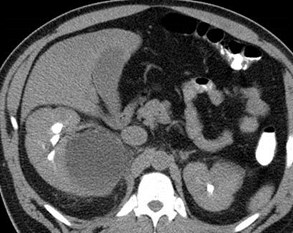
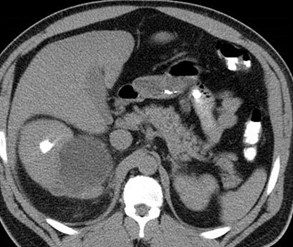
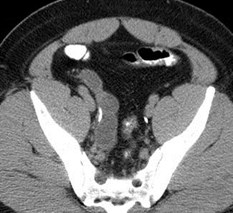
Duplicated right collectingsystem with chronic uppermoiety obstruction, insertioninto prostatic urethra,secondarily infected
Acute right flank pain

Duplication
•Appearance of upper tract predicts site of insertion:normal pelvicaliceal system relates to normallypositioned ureteral orifice. Extremely ectopic ureteralorifice relates to dysplastic, poorly function moiety.
•Most common complications: reflux, ectopicureterocele, ectopic ureteral insertion, UPJ lowermoiety (more in males).
•REFLUX: into lower pole because superior lateralposition results in short intramural segment whichpredisposes to reflux.
•OBSTRUCTION: of upper pole, typically withureterocele and/or ectopic insertion
Fernbach. Radiographics 1997;17:109

Ectopic Ureteral Insertion
•Since upper pole stays with Wolffian duct longer,ureter may insert into Wolffian duct remnant ratherthan bladder
•Males: seminal vesicle, vas deferens, ejaculatoryduct, prostatic urethra
–Extravesical insertions are suprasphincteric producinginfection, inflammation, mass such as epididymitis,orchitis.No enuresis
•Females: vagina, urethra, urethrovaginal septum,Gartner ducts
–Ectopic insertion is beyond spincter, symptoms of dribblingor primary incontinence

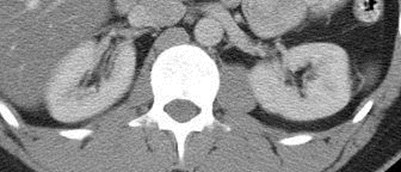
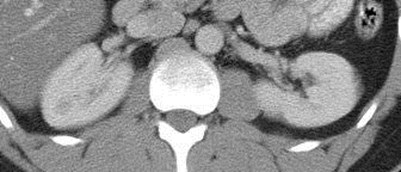
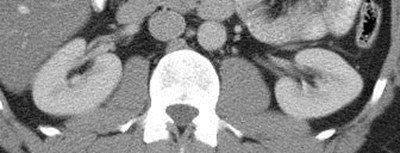
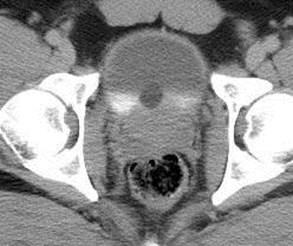
Duplicated rightcollecting systemwith Muellerian cyst

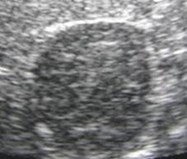
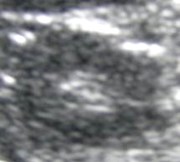
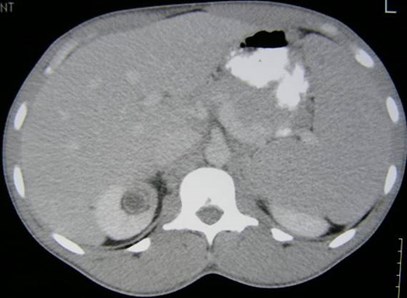
Right Kidney
SUP
MID
INF

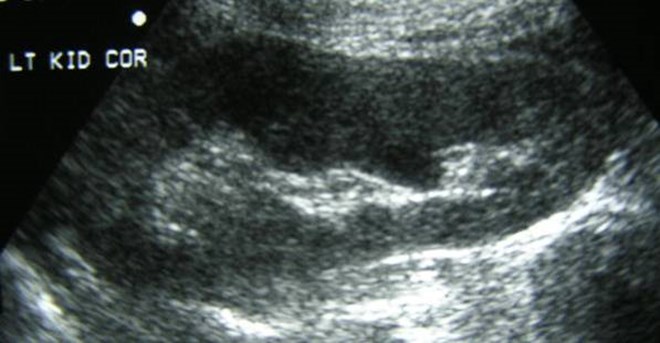

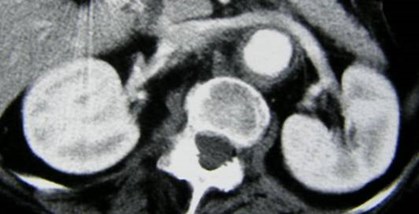
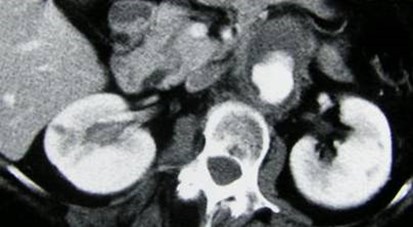
Duplicated right Collecting System
Left Column of Bertin

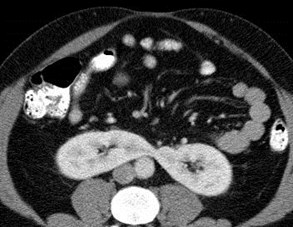
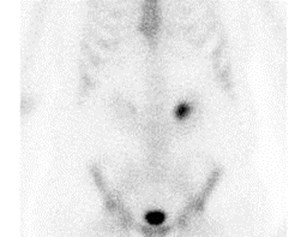
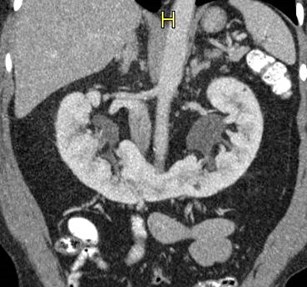
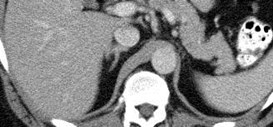
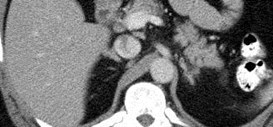
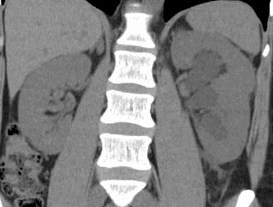
Horseshoe Kidney
Normal Adrenal Glands

Fusion Anomalies: Horseshoe
•Fusion at one pole, 90% lower pole.
•Abnormal fusion probably occurs at 5 – 12 mmembryo stage, when kidneys fuse in pelvis beforerenal capsule has matured.
•Ascent of fused kidney is hindered by IMA
•Most common fusion anomaly, 1/400
•Complications: UPJ obstruction, recurrent infectionsand calculi due to stasis, increased risk of trauma,tumors (Wilm’s tumor, carcinoid, transitional cell CA)
•Other associations: urogenital, GI, neurologic,skeletal, chromosomal (XO, Trisomy 18)

Horseshoe Kidney
•Fusion site or isthmus usually composed ofrenal parenchymal tissue, but can be fibrous
•Isthmus is anterior to aorta and IVC, posteriorto IMA
•Renal pelves are malrotated and lie anteriorly
•Blood vessel variations are common
•Most patients are asymptomatic or presentwith urinary tract infections

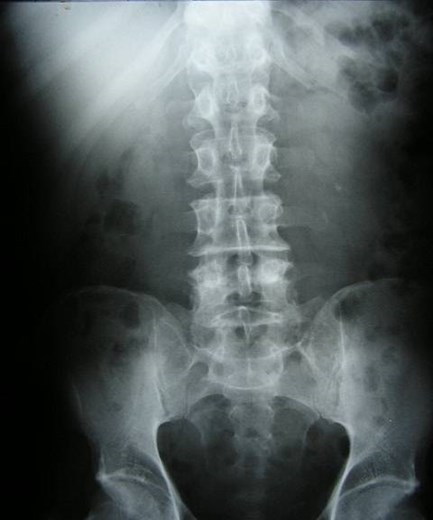

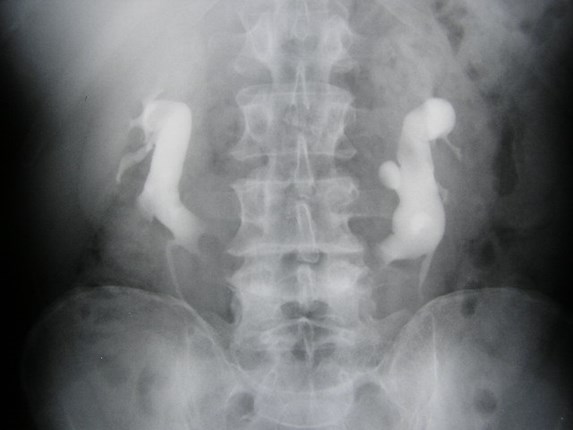
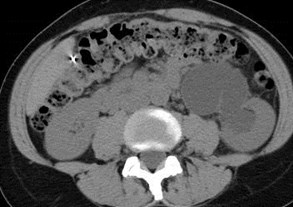
Horseshoe Kidney with non-obstructing left sided calculus

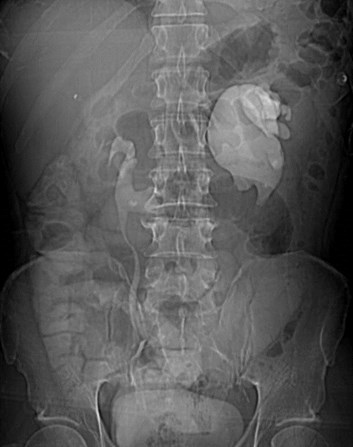
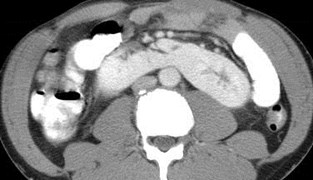
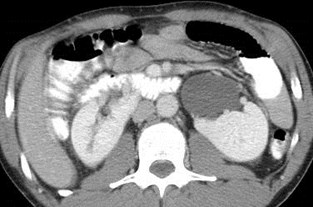
Horseshoe Kidney with dilatedextra renal pelvis/ mild UPJO

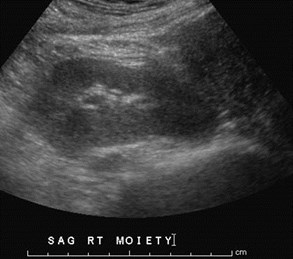
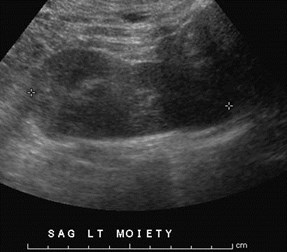
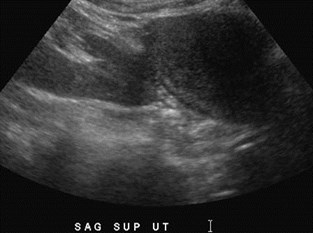
Pancake Kidney just above uterus

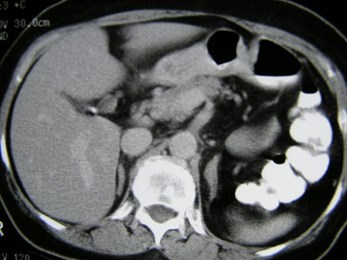
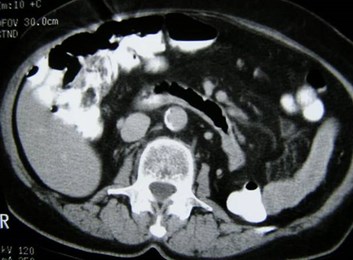
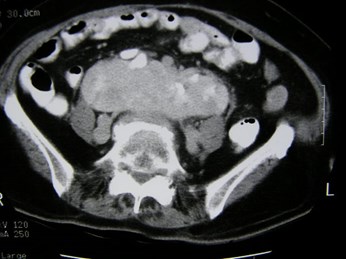
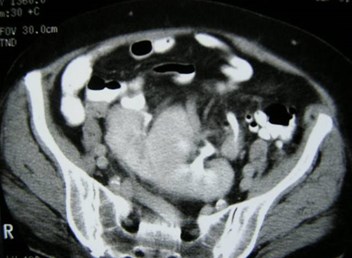
Pancake Kidney, linear adrenal glands

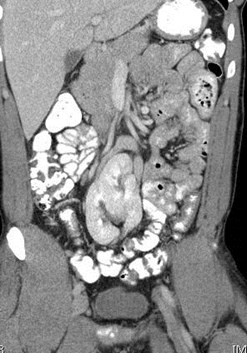
Right Iliac Kidney
BilateralDuplications

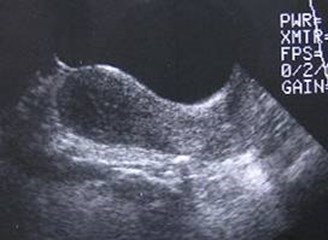
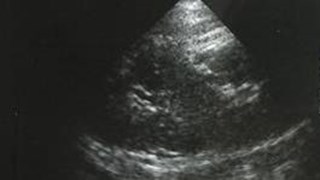
Left renal fossa
24 year old with right pelvic mass
Right Pelvic Kidney
Left Kidney duplicated and malrotated

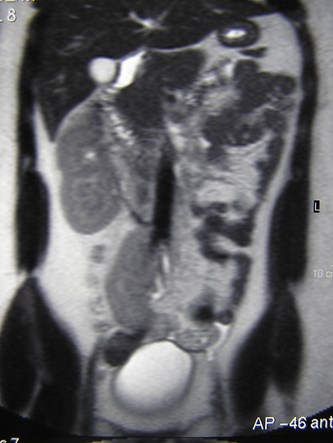
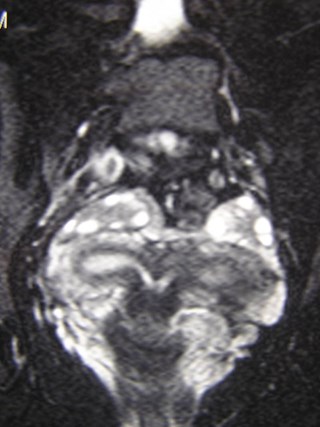
Crossed Renal Ectopia
Bicornuate Uterus

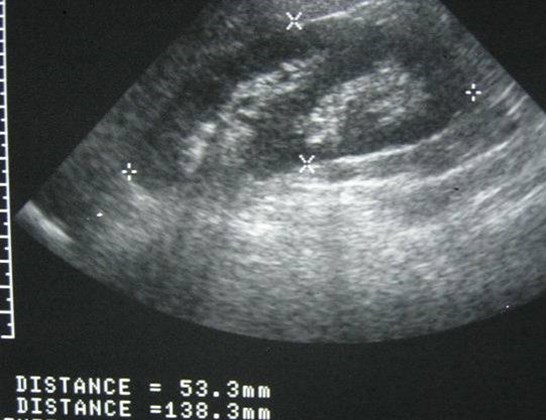
Right Renal Fossa
Empty Left Renal Fossa

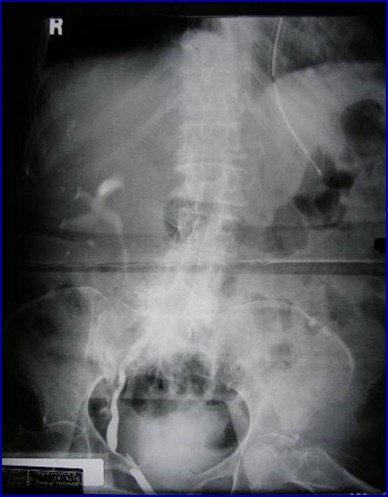

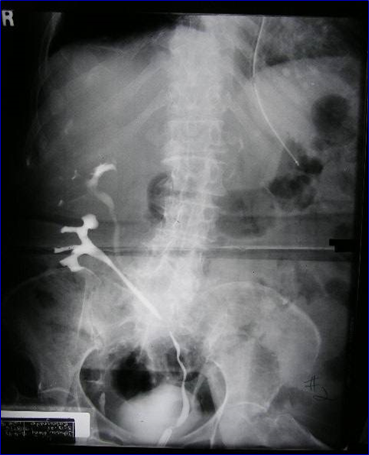
Crossed Fused Ectopia

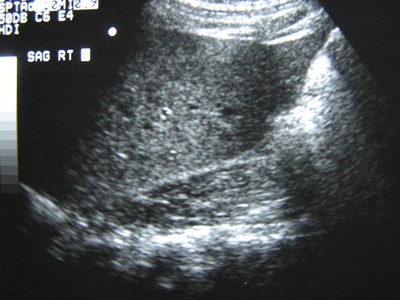
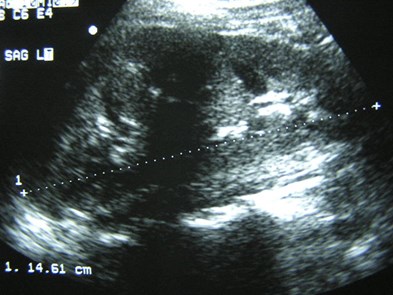
Right Renal Agenesis

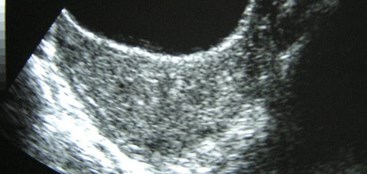
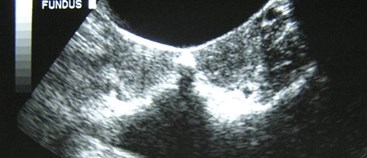
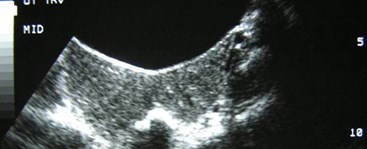
Bicornuate Uterus

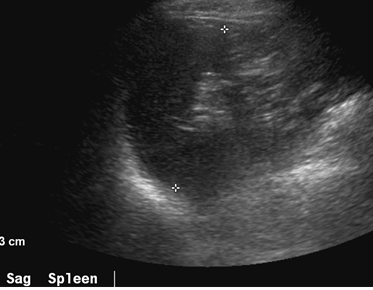
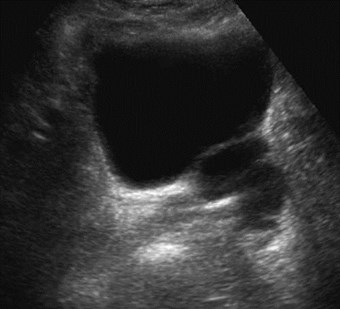
36 year old male
Left renal agenesis
Ipsilateral seminalvesicle cyst

Anomalies of the SeminalVesicles
•Cysts: isolated, associated with upper tract anomaliesor autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
•Usually become apparent in 2nd or 3rd decades withsymptoms of hematuria, hemospermia, epididimytis,prostatitis, infertility, UTIs
•Associated with ipsilateral renal agenesis or dysplasiain 2/3 of patients, reflecting maldevelopment of distalmesonephric duct and faulty ureteral budding withatresia of ejaculatory duct leading to obstruction andcystic dilatation of seminal vesicle
•Differential Dx: true prostate cysts, mullerian ductcysts, prostatic utricle cysts, hydronephrotic pelvickidney, bladder diverticula, ureteroceles
Arora. AJR 2007;189:130

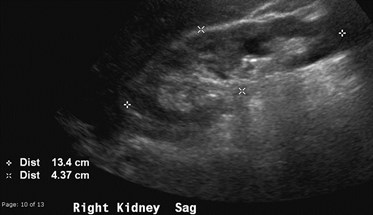
31 year old with microscopic hematuria
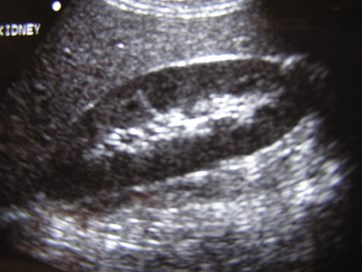
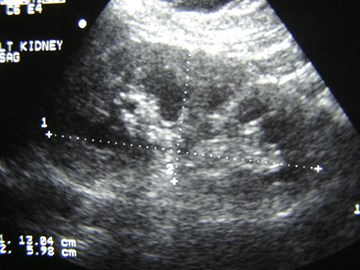
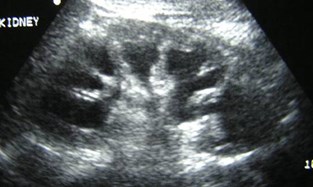
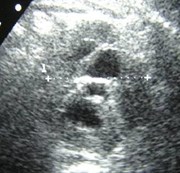
No right kidney visualized

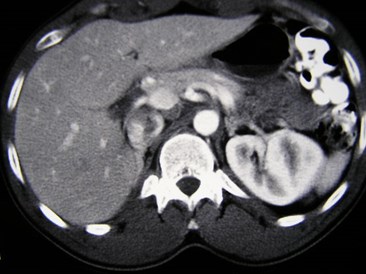
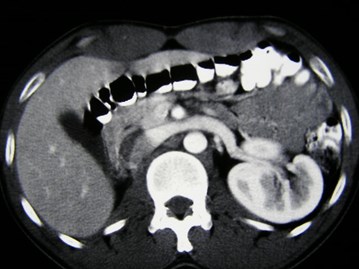
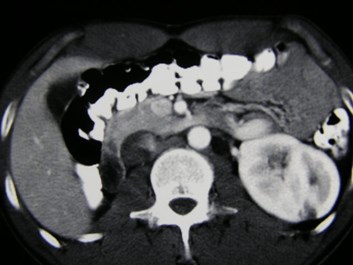
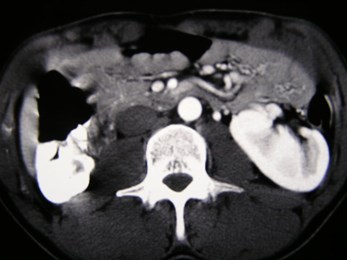

Crossed Fused Ectopia
Versus
Duplicated collectingsystem and absent rightkidney
Need information about ureters to make distinction

Right Kidney
Left Kidney

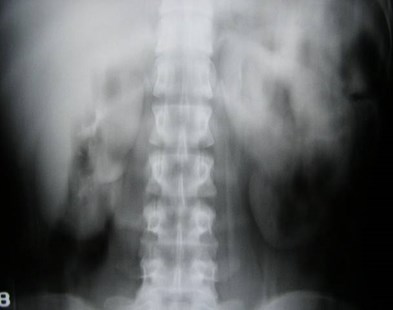
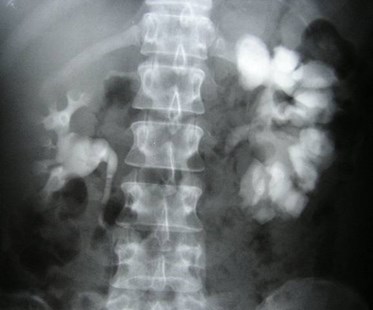
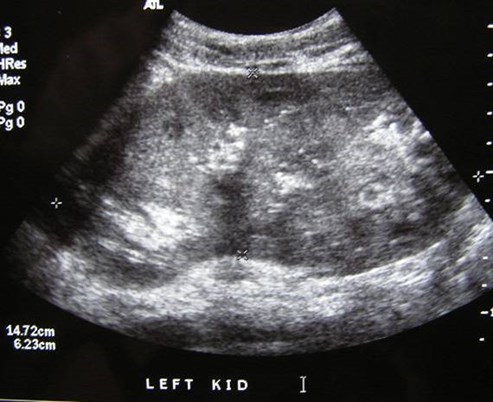
Megacalyces

Megacalyces
•Congenital underdevelopment of papillae leading toincreased number and size of calyces
•Calyces have a faceted or polygonal shape with nofornices or papillary impressions and with hypoplasticmedullary pyramids
•Hypothesis for pathogenesis is anomalous ureteralbud division leading to extra calyces at the expenseof the medullary portion of the kidney
•Diagnosis should be made only in patients withoutprior or concurrent obstruction or reflux.
•Renal function is normal, kidney is large

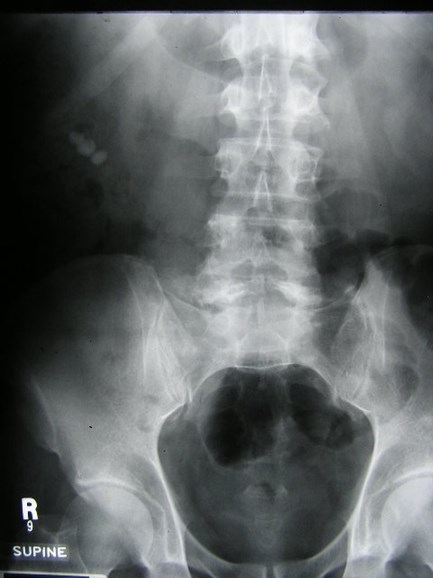

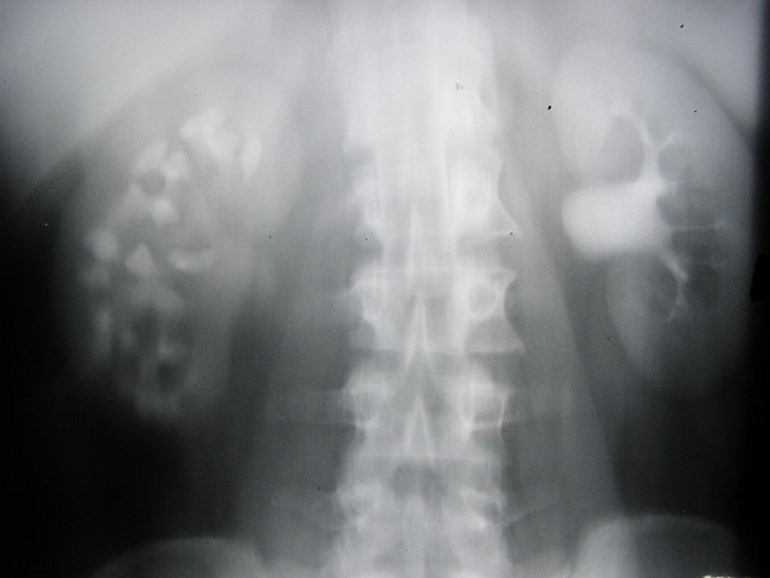

Megacalyces
Non-obstructing right calculi
Left sinus lipomatosis

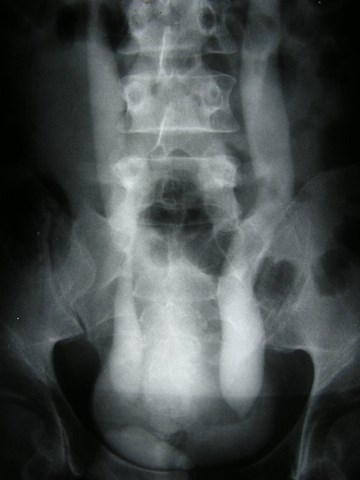
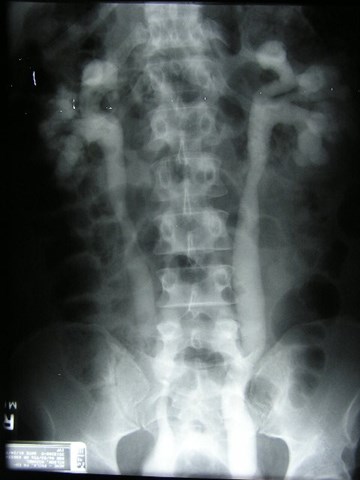
Megaureters

Megaureters
•Enlarged ureter with or without dilatation of uppercollecting system.
•Primary
–Obstructed Primary Ureter: Dilatation above a short(0.5 – 4 cm) aperistaltic, normal caliber ureter withnormal insertion into bladder. Similar to achalasi andHirschprung disease. Cause unknown.
–Refluxing Primary Ureter
–Nonrefluxing unobstructed primary megaureter
•Secondary
–Result of some abnormality such as urethral valves,neurpathic bladder, urethral structure, etc.

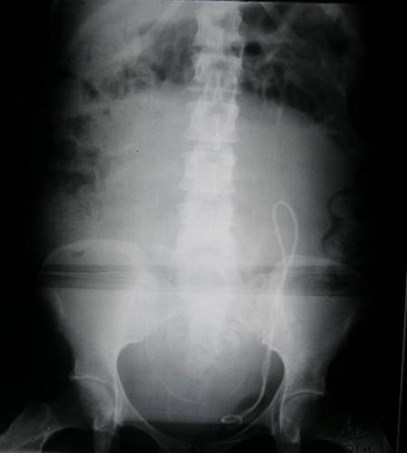
Patient with elevated creatinine

Right Kidney
Left Kidney

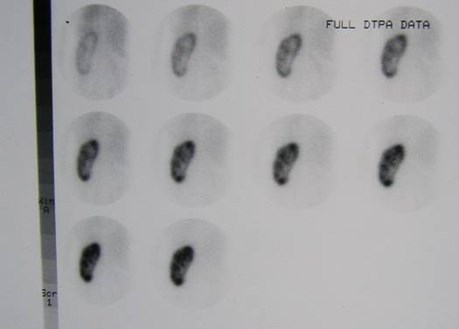
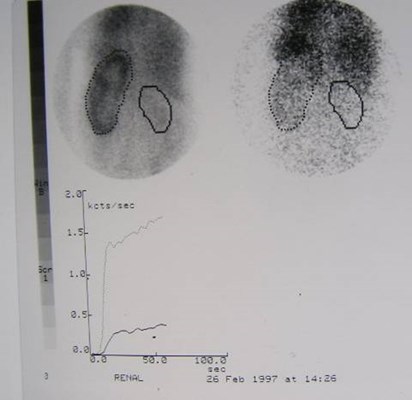

Non-functioning, dysplasticright kidney
UPJ obstruction left kidney inpregnant patient

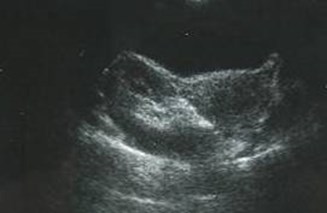
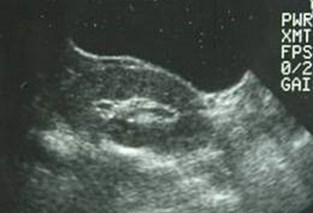
Newborn Cases

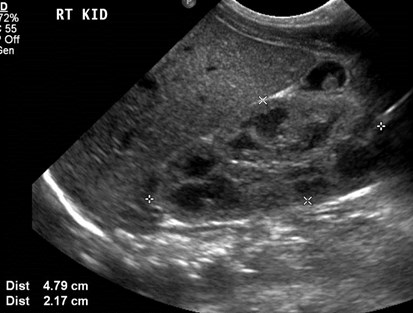
Unilateral MulticysticDysplastic Kidney

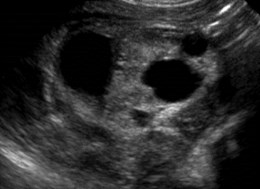
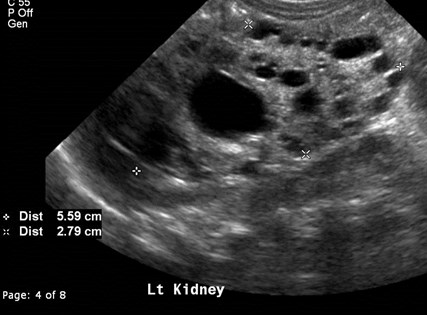
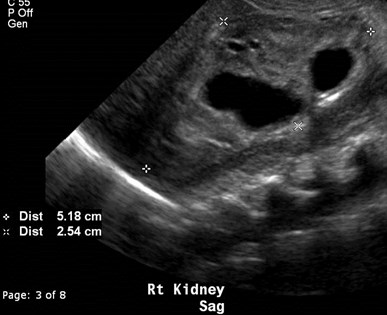
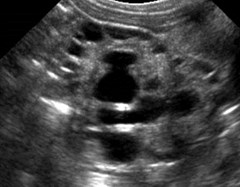

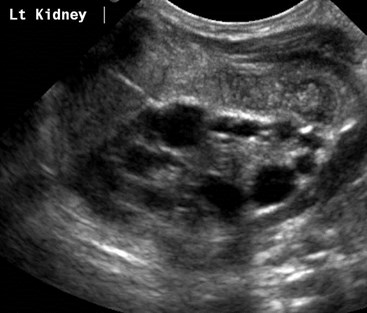
Bilateral Multicystic DysplasticKidneys
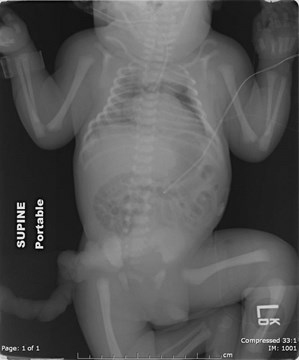
Hypoplastic Lungs

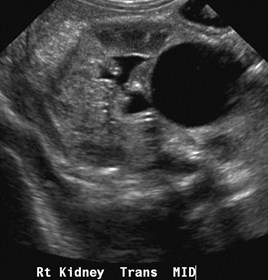
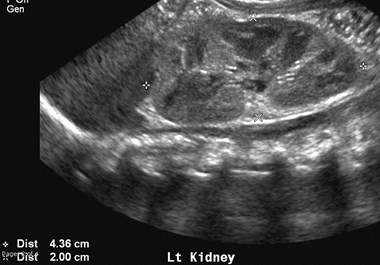
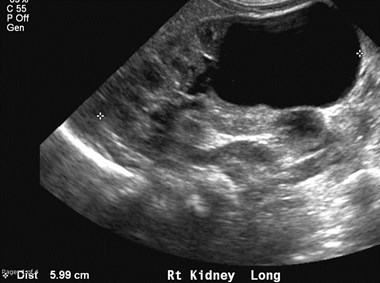
Partial MulticysticDysplastic Kidney

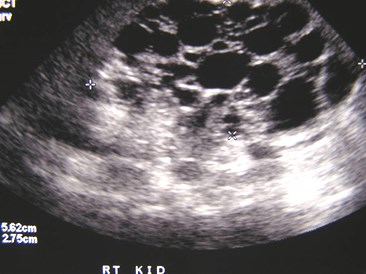
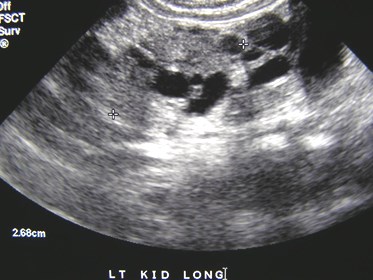
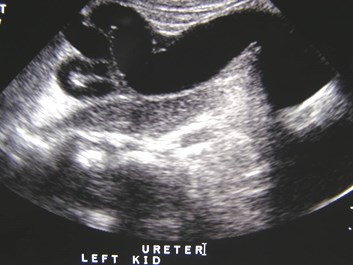
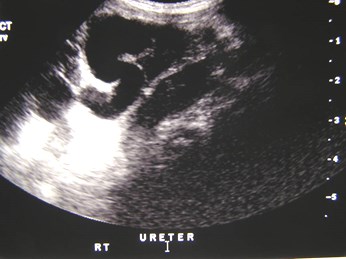

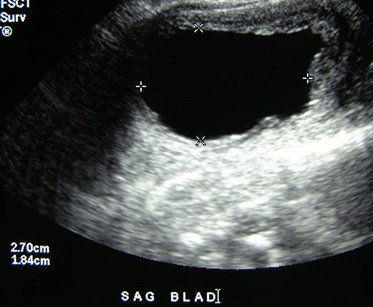
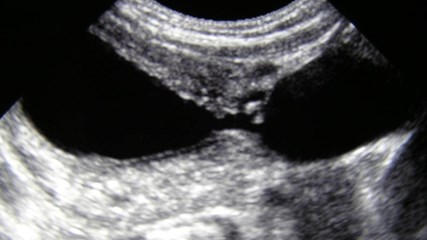
Bilateral Multicystic DysplasticKidneys with dilated ureters 2°posterior urethral valves

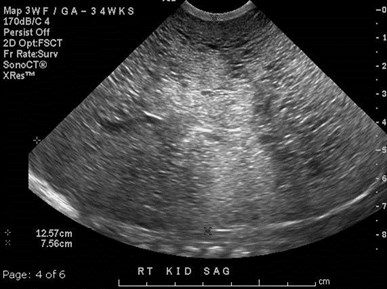
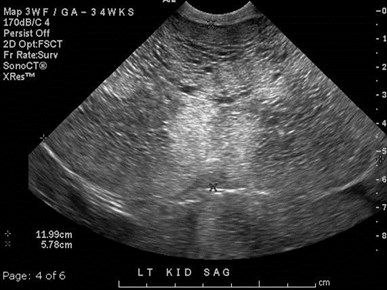

Autosomal Recessive PolycysticKidney Disease

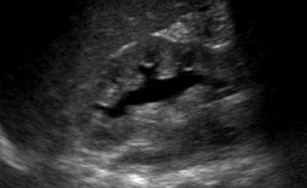
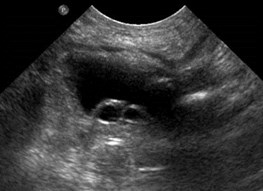
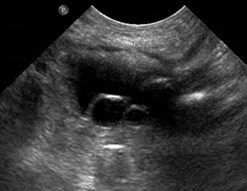
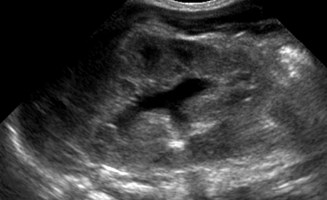
Bilateral hydronephrosis 2° bilateralureteroceles and presumed reflux
Bladder transverse every few seconds

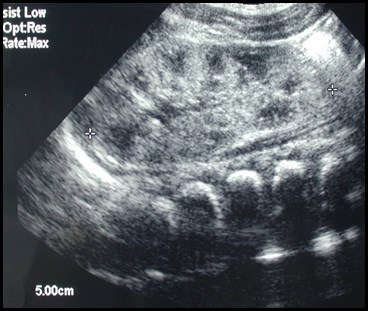
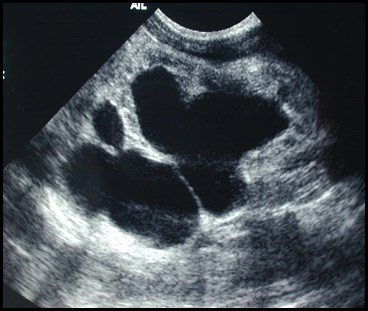
Newborn with abnormal prenatal sonogram

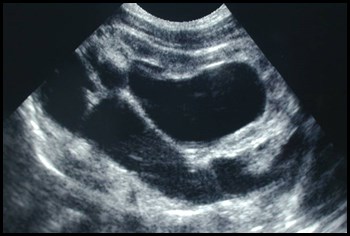
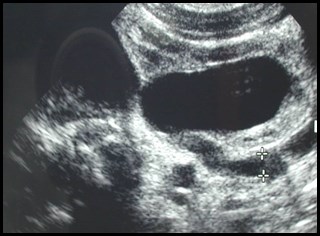
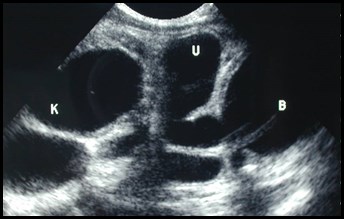
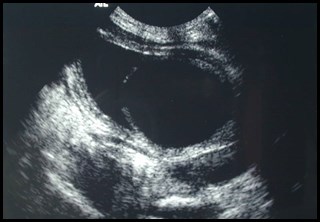

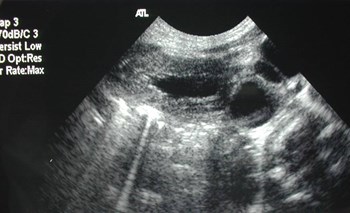
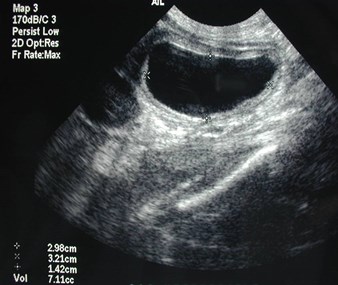
Post voidbladder
Post voidureterocele
Duplicated collecting system with obstructed
upper pole moiety ending in a ureterocele and
reflux into lower pole moiety


The End
Scottish Highlands, June 2007